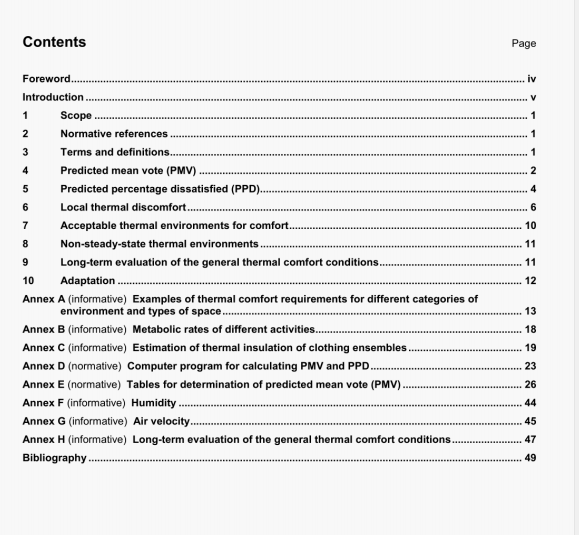
ISO 7194:2008 pdf download.Measurement of fluid flow in closed conduits - velocity-area methods of flow measurement in swirling or asymmetric flow conditions in circular ducts by means of current-meters or Pitot static tubes.
It specifies the measurements required, the precautions to be taken, the corrections to apply, and describes the additional uncertainties which are introduced when a measurement in asymmetric or swilling flow has to be made
Only flows with a negligible radial component are considered, however. Furthermore, it is not possible to make a measurement in accordance with this International Standard if, at any point in the measunng cross-section. the local velocity makes an angle of greater than 40° with the axis of the duct, or where the index of asymmetry (defined in Annex F) is greater than 0.15.
Thee International Standard deals only with Instruments for measunng local velocity as defined In ISO 3354 and ISO 3966. It Pitot static tubes are used, this International Standard applies only to flows where the Mach number corresponding to local velocities does not exceed 0.25.
2 Normative references
The following referenced documents are indispensable for the application of this document. For dated references, only the edition cited apphes For undated references, the latest edition of the referenced document (including any amendments) applies.
ISO1TR 3313, Measurement of fluid flow in closed conduits — Guidelines on the effects of flow pulsations on flow-measurement instruments
ISO 3354:2008, Measurement of clean water flow in closed conduits — Velocity-area method using current- meters in full conduits and under regular flow conditions
ISO 3455:2007, Hydrometry — Calibration of current-meters in straight open tanks
ISO 3966:2008, Measurement of fluid flow in closed conduits — Velocity area method using Pitot static tubes
ISO 4006. Measurement of fluid flow in closed conduits — Vocabulary and symbols
ISO 5168, Measurement of fluid flow — Procedures for the evaluation of uncertainties.
Only flows with a negligible radial component are considered, however. Furthermore, it is not possible to make a measurement in accordance with this International Standard if, at any point in the measunng cross-section. the local velocity makes an angle of greater than 40° with the axis of the duct, or where the index of asymmetry (defined in Annex F) is greater than 0.15.
Thee International Standard deals only with Instruments for measunng local velocity as defined In ISO 3354 and ISO 3966. It Pitot static tubes are used, this International Standard applies only to flows where the Mach number corresponding to local velocities does not exceed 0.25.
2 Normative references
The following referenced documents are indispensable for the application of this document. For dated references, only the edition cited apphes For undated references, the latest edition of the referenced document (including any amendments) applies.
ISO1TR 3313, Measurement of fluid flow in closed conduits — Guidelines on the effects of flow pulsations on flow-measurement instruments
ISO 3354:2008, Measurement of clean water flow in closed conduits — Velocity-area method using current- meters in full conduits and under regular flow conditions
ISO 3455:2007, Hydrometry — Calibration of current-meters in straight open tanks
ISO 3966:2008, Measurement of fluid flow in closed conduits — Velocity area method using Pitot static tubes
ISO 4006. Measurement of fluid flow in closed conduits — Vocabulary and symbols
ISO 5168, Measurement of fluid flow — Procedures for the evaluation of uncertainties.