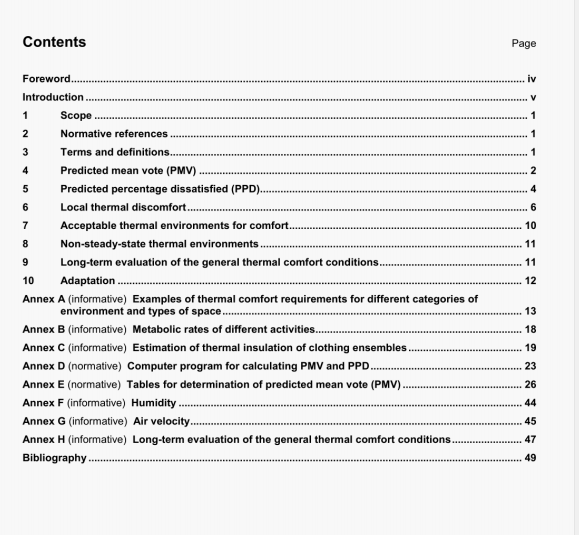
ISO 20963:2005 pdf download.Soil quality - Effects of pollutants on insect larvae (Oxythyrea funesta)-Determination of acute toxicity.
6.3 Larvae food. i.e. dried and finely round cow-dung, no piece larger than 1 mm.
The cow-dung shall come from healthy animals WhiCh have not received any treatment (antibiotics, growth promoters) during a two-week period preceding the date of sampling, It should be verified especially thai animals have not recently been treated against intestinal worms.
6.4 Reference substance, i.e. 2.4,5-trichlorophenol of recognised analytical grade.
7 Apparatus
Use usual laboratory equipment and the following materials.
7.1 Glass containers of capacity about 0,5 Ito 11. covered with a polyethylene membrane (7.5) to allow exchange between the medium and the atmosphere.
7.2 Crusher, or any other apparatus to oblawi food as described in 6.3.
7.3 Larg. scale laboratory mixer for the preparation of the test substrate (6.2).
7.4 Precision balance with an accuracy of at least 1 mg.
7.5 Polyethylene membrane, perforated with small holes to allow exchange between the medium and the
atmosphere.
8 Procedure
8.1 Test design
8.1.1 PrelIminary test
Carry out this test over a large range of dilutions/concentrations (e.g. contaminated soils: 0 %. 1 %. 5 %. 25 %. 50 %, 75 %. 100%: substances’ 0 mglkg, 1 mgPKg, 10 mglkg, 100 mglkg, 1000 mglkg).
Substances are usually not tested at concentrations higher than 1 000 mglkg (dry mass of test substrate).
Use preliminary test results to select the range of dilutions/concentrations for the final test. In order to establish this range, the highest concentration at which no lethal effect Is observed and the lowest concentration at wh.ch 100 % mortality is observed should be determined.
Conduct the preliminary test without replication.
When no effects are observed, even at a concentration of 1 000 mgilg, the definitive test can be designed as
a limit test.
8.1.2 Definitive test
Select a range of at least five dilutions/concentrations of the contaminated soil or the test substance, providing a geometric progression between the highest dilution/concentration causing no mortality and the lowest dilution/concentration causing 100 % mortality In the preliminary test The ratio between two consecutive concentrations should not exceed two.
The cow-dung shall come from healthy animals WhiCh have not received any treatment (antibiotics, growth promoters) during a two-week period preceding the date of sampling, It should be verified especially thai animals have not recently been treated against intestinal worms.
6.4 Reference substance, i.e. 2.4,5-trichlorophenol of recognised analytical grade.
7 Apparatus
Use usual laboratory equipment and the following materials.
7.1 Glass containers of capacity about 0,5 Ito 11. covered with a polyethylene membrane (7.5) to allow exchange between the medium and the atmosphere.
7.2 Crusher, or any other apparatus to oblawi food as described in 6.3.
7.3 Larg. scale laboratory mixer for the preparation of the test substrate (6.2).
7.4 Precision balance with an accuracy of at least 1 mg.
7.5 Polyethylene membrane, perforated with small holes to allow exchange between the medium and the
atmosphere.
8 Procedure
8.1 Test design
8.1.1 PrelIminary test
Carry out this test over a large range of dilutions/concentrations (e.g. contaminated soils: 0 %. 1 %. 5 %. 25 %. 50 %, 75 %. 100%: substances’ 0 mglkg, 1 mgPKg, 10 mglkg, 100 mglkg, 1000 mglkg).
Substances are usually not tested at concentrations higher than 1 000 mglkg (dry mass of test substrate).
Use preliminary test results to select the range of dilutions/concentrations for the final test. In order to establish this range, the highest concentration at which no lethal effect Is observed and the lowest concentration at wh.ch 100 % mortality is observed should be determined.
Conduct the preliminary test without replication.
When no effects are observed, even at a concentration of 1 000 mgilg, the definitive test can be designed as
a limit test.
8.1.2 Definitive test
Select a range of at least five dilutions/concentrations of the contaminated soil or the test substance, providing a geometric progression between the highest dilution/concentration causing no mortality and the lowest dilution/concentration causing 100 % mortality In the preliminary test The ratio between two consecutive concentrations should not exceed two.