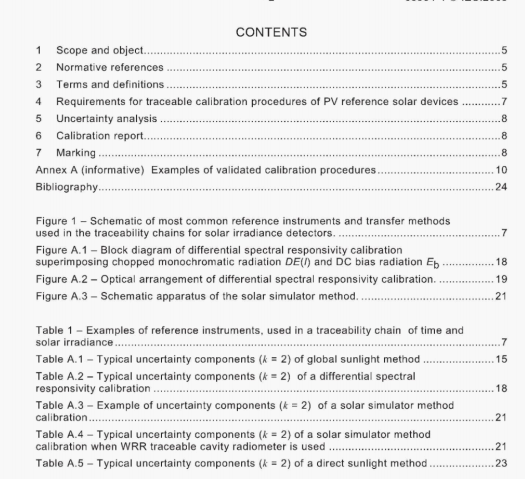
BS EN 14359:2006 pdf download.Gas-loaded accumulators for fluid power applications.
3.1 Terms and definitions
For the purpose of this document the following terms and definitions apply.
3.1.1
gas-loaded accumulator
hydraulic accumulator with separator between liquid and gas where the liquid Is pressurized using the compressibility of an inert gas (for example nitrogen), The separator can be a bladder, a diaphragm or a piston,
Gas-loaded accumulators have shells, which can consist of cylinders, dished ends and flat plates. Openings are always isolated, located on the axis centre line and positioned at both ends of the accumulator It is assumed that such vessels are axis-symmetrical
3.1.2
bladder accumulator
gas-loaded accumulator consisting of pressure-retaining shell, either spun-forged from seamless tube. hammer-forged from hollow bar or of welded construction, in which the liquid and gas are separated by a flexible bag or bladder normally retained at one end of the shell
3.1.3
diaphragm accumulator
gas-loaded accumulator consisting of pressure-retaining shell assembly, in which the construction can either be screwed or welded, with integral ports in which the liquid and gas are separated by a flexible membrane normally retained at its largest diameter to the shell
3.1.4
piston accumulator
gas-loaded accumulator consisting of cylinder body and end cap assemblies in which the liquid and gas are separated by a rigid sliding piston
3.1.5
transfer type accumulator
gas-loaded accumulator with a port for connecting additional gas capacity from one or more gas bottle(s)
3.1.6
gas bottle
inter-connected pressure vessels consisting of body and, depending upon construction, port assemblies used to provide additional gas capacity and communicating with the gas chamber of the accumulator by means of a pipe connection.
For the purpose of this document the following terms and definitions apply.
3.1.1
gas-loaded accumulator
hydraulic accumulator with separator between liquid and gas where the liquid Is pressurized using the compressibility of an inert gas (for example nitrogen), The separator can be a bladder, a diaphragm or a piston,
Gas-loaded accumulators have shells, which can consist of cylinders, dished ends and flat plates. Openings are always isolated, located on the axis centre line and positioned at both ends of the accumulator It is assumed that such vessels are axis-symmetrical
3.1.2
bladder accumulator
gas-loaded accumulator consisting of pressure-retaining shell, either spun-forged from seamless tube. hammer-forged from hollow bar or of welded construction, in which the liquid and gas are separated by a flexible bag or bladder normally retained at one end of the shell
3.1.3
diaphragm accumulator
gas-loaded accumulator consisting of pressure-retaining shell assembly, in which the construction can either be screwed or welded, with integral ports in which the liquid and gas are separated by a flexible membrane normally retained at its largest diameter to the shell
3.1.4
piston accumulator
gas-loaded accumulator consisting of cylinder body and end cap assemblies in which the liquid and gas are separated by a rigid sliding piston
3.1.5
transfer type accumulator
gas-loaded accumulator with a port for connecting additional gas capacity from one or more gas bottle(s)
3.1.6
gas bottle
inter-connected pressure vessels consisting of body and, depending upon construction, port assemblies used to provide additional gas capacity and communicating with the gas chamber of the accumulator by means of a pipe connection.